Lessico
Germania Inferiore
Germania Inferior
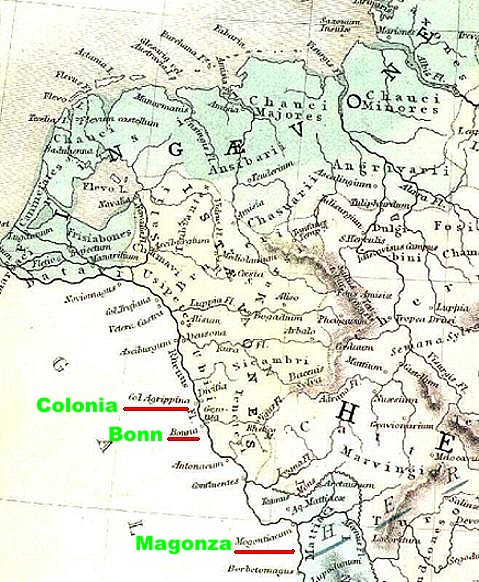
Nel 90 dC furono costituite le due province romane della Germania Inferiore con capitale Colonia (51° parallelo nord) e della Germania Superiore con capitale Magonza (50° parallelo nord). Le due capitali distavano - e distano - fra loro 140 km in linea d'aria.
Da nord
a sud gli insediamenti principali della Germania Inferiore erano i seguenti: Forum Hadriani (coś denominato dall'imperatore Adriano![]() durante un suo viaggio nel 121 dC, oggi Voorburg che fa parte
dell'agglomerato urbano dell'Aia), Trajectum ad Rhenum (Utrecht, 182 km in linea d'aria da Colonia), Noviomagus
Batavorum (Nimega), Colonia Ulpia Traiana e il vicino castrum di Vetera (Xanten),
Novaesium (Neuss), Colonia
Agrippinensis (Colonia, la capitale della provincia, dove nel 1280 moŕ
Alberto Magno
durante un suo viaggio nel 121 dC, oggi Voorburg che fa parte
dell'agglomerato urbano dell'Aia), Trajectum ad Rhenum (Utrecht, 182 km in linea d'aria da Colonia), Noviomagus
Batavorum (Nimega), Colonia Ulpia Traiana e il vicino castrum di Vetera (Xanten),
Novaesium (Neuss), Colonia
Agrippinensis (Colonia, la capitale della provincia, dove nel 1280 moŕ
Alberto Magno![]() ) e
Bonna (Bonn).
) e
Bonna (Bonn).
La
provincia venne affidata a un legatus Augusti pro praetore, un
governatore di provincia imperiale di rango senatorio munito di imperium
delegato dal principe, come stabilito da Augusto![]() nel 27
aC. Nella successiva riorganizzazione tetrarchica
voluta da Diocleziano (fine del III secolo), la Germania Inferiore
divenne parte della Diocesi delle Gallie con il nuovo nome di Germania II.
nel 27
aC. Nella successiva riorganizzazione tetrarchica
voluta da Diocleziano (fine del III secolo), la Germania Inferiore
divenne parte della Diocesi delle Gallie con il nuovo nome di Germania II.
Germania
Inferior was a Roman province
located on the left bank of the Rhine, in today's Luxembourg, southern
Netherlands, parts of Belgium, and North Rhine-Westphalia left of the Rhine.
The principal settlements of the province were Castra Vetera and Colonia Ulpia
Traiana (both near Xanten), Coriovallum (Heerlen), Albaniana (Alphen aan den
Rijn), Lugdunum Batavorum (Katwijk), Forum Hadriani (Voorburg, the northern-most Roman
city on the European continent and the second oldest city of The
Netherlands, named Forum Hadriani - Hadrian’s Market - in 121 AD by emperor
Hadrian![]() who made a long voyage along the northwestern border of the empire), Ulpia
Noviomagus Batavorum (Nijmegen), Traiectum (Utrecht), Atuatuca Tungrorum (Tongeren),
Bonna (Bonn), and Colonia Agrippinensis (Cologne), the capital of Germania
Inferior.
who made a long voyage along the northwestern border of the empire), Ulpia
Noviomagus Batavorum (Nijmegen), Traiectum (Utrecht), Atuatuca Tungrorum (Tongeren),
Bonna (Bonn), and Colonia Agrippinensis (Cologne), the capital of Germania
Inferior.
The army of Germania Inferior, known from inscriptions simply as EX.GER.INF. (Exercitus Germania Inferior), had several legions at its service: of these, the Legions I Minervia and XXX Ulpia Victrix were the most permanent. The Roman Navy's Classis Germanica, charged with patrolling the Rhine and the North Sea coast, was based in Castra Vetera and later in Agrippinensis.
The first confrontations between a Roman army and the peoples of Germania Inferior occurred during Julius Caesar's Gallic Wars. Caesar invaded the region in 57 BC and in the next three years annihilated several tribes, including the Eburones and the Menapii, whom Caesar called "Germanic" but who probably were Celtic or at least mixed Celtic-Germanic. Germanic influence increased during Roman times, leading to the assimilation of all Celtic peoples in the area. Germania Inferior had Roman settlements since approximately 50 BC and was at first part of Gallia Belgica; it was established as a Roman province in the year 90, later becoming an Imperial province. It lay north of Germania Superior, together with which it made up Germania. The epithet Inferior refers to its downstream position. After the final abandonment of the province it became the core of the Frankish Kingdom.